Abstract
This paper proposes a novel Reinforcement Learning (RL) approach for sim-to-real policy transfer of Vertical Take-Off and Landing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (VTOL-UAV). The proposed approach is designed for VTOL-UAV landing on offshore docking stations in maritime operations. VTOL-UAVs in maritime operations encounter limitations in their operational range, primarily stemming from constraints imposed by their battery capacity. The concept of autonomous landing on a charging platform presents an intriguing prospect for mitigating these limitations by facilitating battery charging and data transfer. However, current Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) methods exhibit drawbacks, including lengthy training times, and modest success rates. In this paper, we tackle these concerns comprehensively by decomposing the landing procedure into a sequence of more manageable but analogous tasks in terms of an approach phase and a landing phase. The proposed architecture utilizes a model-based control scheme for the approach phase, where the VTOL-UAV is approaching the offshore docking station. In the Landing phase, DRL agents were trained offline to learn the optimal policy to dock on the offshore station. The Joint North Sea Wave Project (JONSWAP) spectrum model has been employed to create a wave model for each episode, enhancing policy generalization for sim2real transfer. A set of DRL algorithms have been tested through numerical simulations including value-based agents and policy-based agents such as Deep Q Networks (DQN) and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) respectively. The numerical experiments show that the PPO agent can learn complicated and efficient policies to land in uncertain environments, which in turn enhances the likelihood of successful sim-to-real transfer.
 |
Ali, Gupta, Hashim Deep Reinforcement Learning for sim-to-real policy transfer of VTOL-UAVs offshore docking operations |
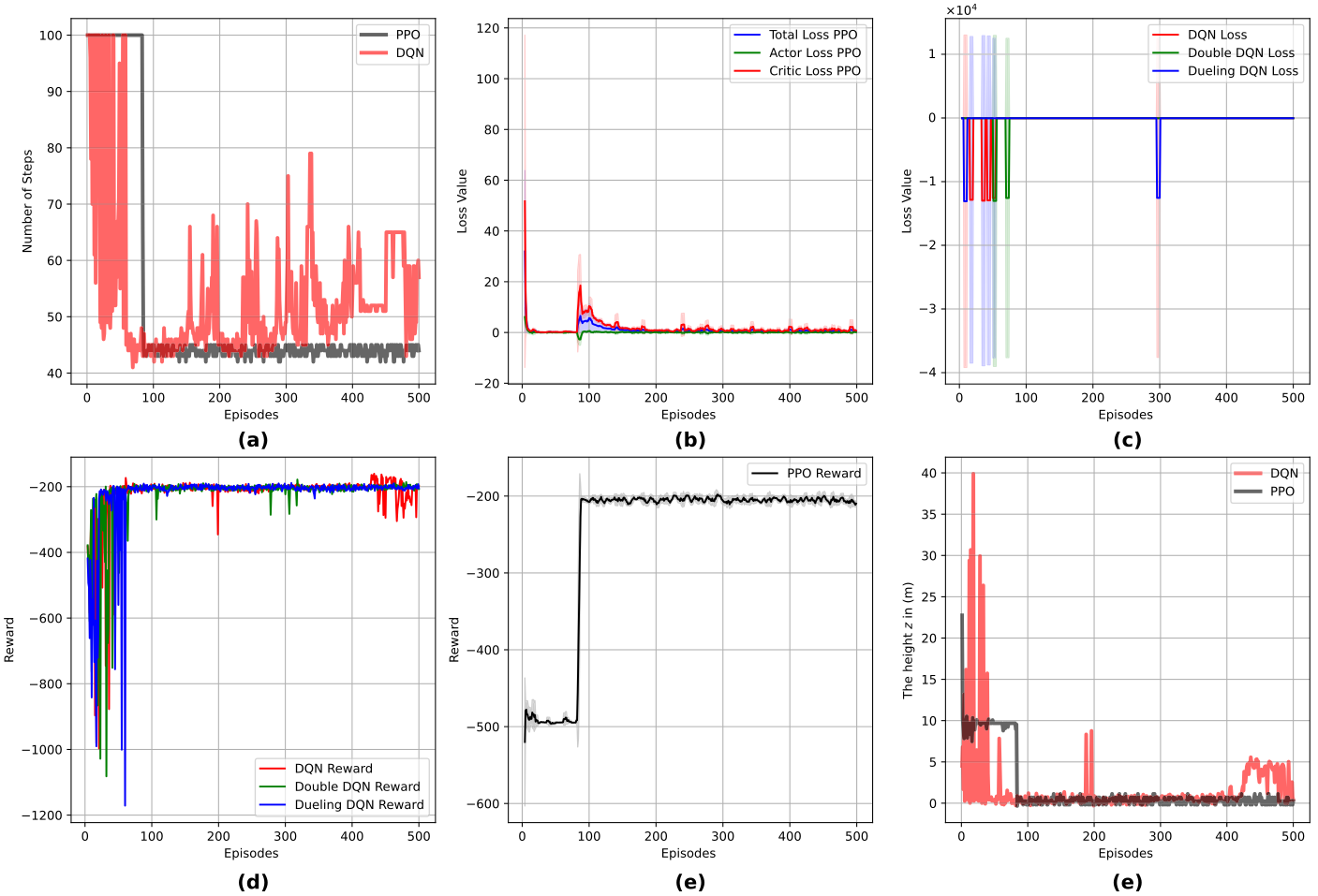
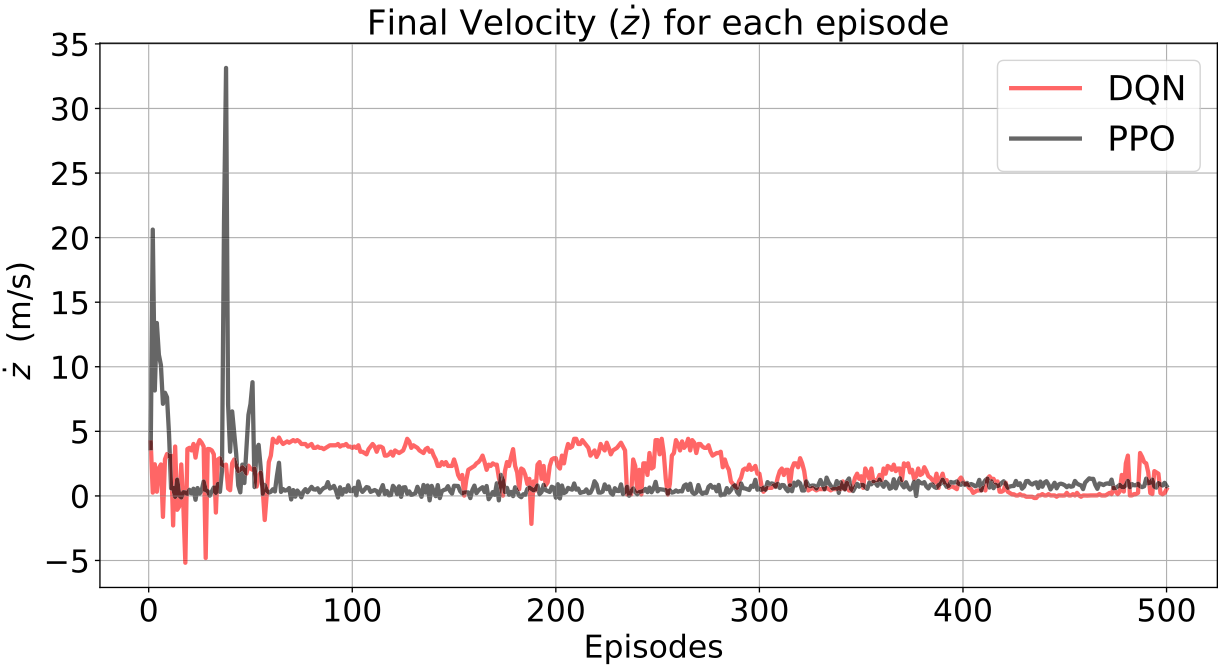
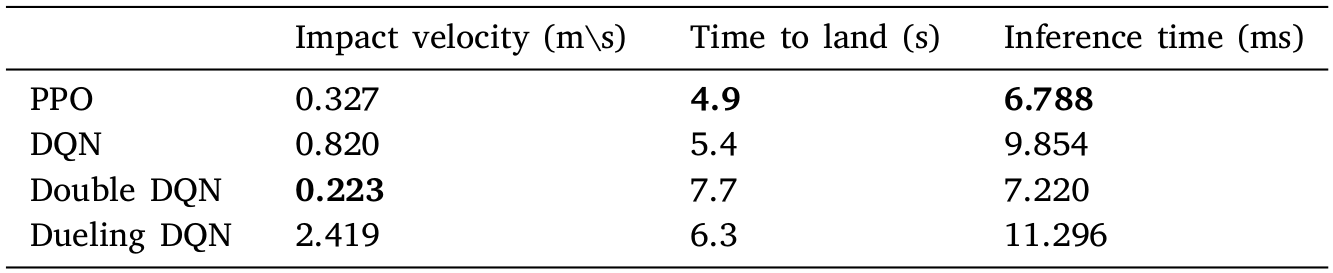
Results
|
|